Understanding the drivers of change that shape the environment we live in and interact with policy can help improve strategic decision-making and lead to better outcomes for the environment and people.
Blog post by Owen White
A new report on drivers of change for Europe’s environment
The European Environment Agency (EEA) has published a report which identifies and describes Drivers of change of relevance for Europe's environment and sustainability. The report was developed with the support of CEP (working with partners Futureline, Fraunhofer, the German Environment Agency, the University of Bergen, and the University of Barcelona). The report recognises that Europe exists within an increasingly complex and uncertain world and that the current state, and future outlook of Europe’s environment is influenced by a range of environmental but also non-environmental ‘drivers of change’. As the world is increasingly ‘interconnected through flows of information, resources, goods and services, people and ideas’ these drivers often originate outside Europe.
Environmental policy and strategy has often focused on specific outcomes, such as meeting an air quality target, often in isolation of wider system considerations. More recently broader and longer-term policy ambitions have emerged, such as the UN Sustainable Development Goals, the 7th European Action Programme, the European Green Deal, and in the UK the 25 Year Environment Plan. At the same time, there has been an increased interest in understanding better the systemic nature of many environmental challenges, and integrating approaches such as systems thinking, foresight and horizon scanning into the process of environmental policy-making.
By identifying key drivers of change for the environment and sustainability in a systematic and systemic way, this new report aims to provide a sound knowledge base for decision-making and ‘information concerning possible future scenarios and implications, so to better support policy-makers in anticipating issues, managing risks and chasing opportunities’.
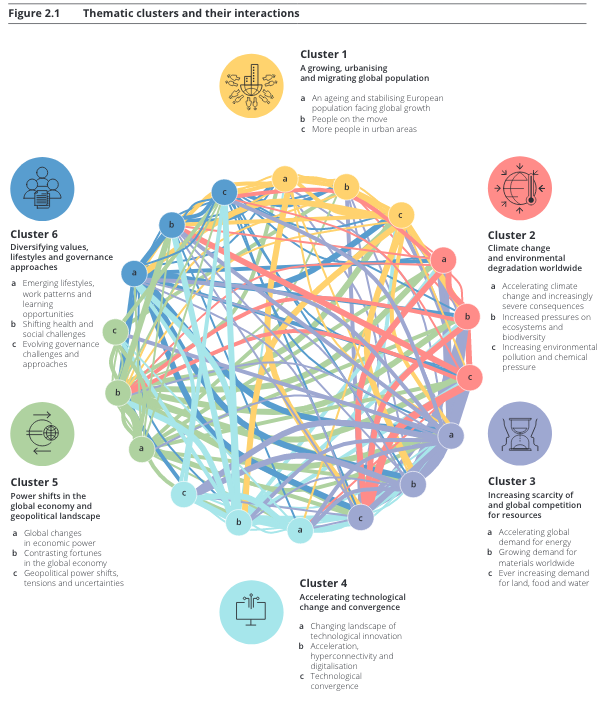
Six clusters of drivers of change are defined and described in detail, including interactions within and across clusters (see figure):
1. A growing, urbanising and migrating global population
2. Climate change and environmental degradation worldwide
3. Increasing scarcity of and global competition for resources
4. Accelerating technological change and convergence
5. Power shifts in the global economy and geopolitical landscape
6. Diversifying values, lifestyles and governance approaches
The report presents a timely reflection on Europe and European countries place in a rapidly changing world. The ongoing Covid-19 pandemic provides a stark reminder of the impact external factors can have on society. The report in fact identified an increased risk of epidemics and potential for new global pandemics.
More broadly, the report highlights some of the key changes that are emerging in the global and European landscape, and how Europe and European countries might need to respond to the challenges, risks and opportunities these changes imply. It identifies the increasingly complex and interconnected nature of many of the economic, social and environmental challenges we face and the need to tackle these in a systemic way, by transforming production and consumption systems, such as for mobility, energy and food. The EEA intends to use this report as the basis for further research into the implications of drivers of change in Europe, focusing on key priority areas including: the move from a linear to a circular economy; sustainability in the food system ‘from farm to fork'; future proofing energy, buildings and mobility; and to help ensure a socially fair transition.
CEP supporting clients in understanding drivers of change and their implications
For this report CEP worked collaboratively with the EEA to identify, collate and cluster potential drivers of change through a combination of expert knowledge and desk-based research. Once agreed the clusters of drivers were then developed in consultation with a senior expert advisory board and EEA staff. The work drew on a wide range of sources including: indicators and trends; projections (e.g. for population); outlooks or scenarios (such as for climate change or technological developments); and research by academic, NGOs/civil society, international institutions and policy institutions (e.g. the European Commission).
The report builds on more than decade of work by CEP in this area for the EEA, European Commission and national clients. This includes identifying and characterising assessments of global megatrends (global, long‑term trends that are slow to form but have a major impact) as part of the EEA’s flagship European state of the environment reporting (SOER) in 2010 and 2015. CEP has also worked with clients to design and implement methodologies to better understand the implications of drivers of change and emerging issues for the environment and environmental policy. This includes:
Developing a methodology to understand the implications of global megatrends at the national level, and adapting and applying this method in Slovenia and the Western Balkans.
Supporting the design and implementation of the European Foresight System for Emerging Environmental Issues (FORENV).
CEP have also recently been appointed with Cranfield University as a supplier to the new ‘Futures Framework’ which is supporting departments and agencies across UK Government in undertaking futures work and developing foresight capabilities. The support will include understanding: emerging trends and developments that could impact policy; systemic consequences of policy or strategy; and, underlying drivers and issues in scoping policy or strategy.
CEP’s approach to understanding the implications of drivers of change is based around participatory expert insight (through workshops or consultations) combined with thorough desk-based research to draw on the best available evidence. We work with clients to understand their needs, and tailor our approach accordingly. We also seek to include a capacity building element in our work, for example delivering a half-day training session for the Slovenian Ministry of the Environment on using systems thinking as a tool for participatory decision-making as part of our work on understanding the implications of global megatrends for the environment in Slovenia.
For more information contact Owen White (Technical Director).